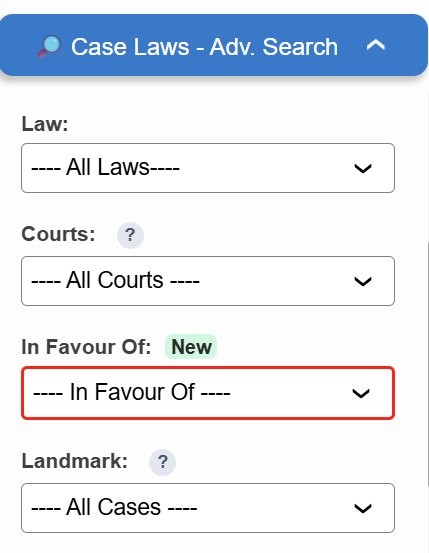
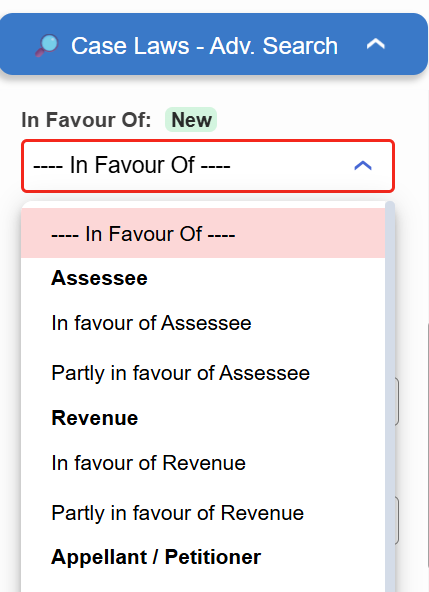
Introducing the “In Favour Of” filter in Case Laws.
- ⚖️ Instantly identify judgments decided in favour of the Assessee, Revenue, or Appellant
- 🔍 Narrow down results with higher precision
Try it now in Case Laws →
Just a moment...
Introducing the “In Favour Of” filter in Case Laws.
Try it now in Case Laws →


Press 'Enter' to add multiple search terms. Rules for Better Search
No Folders have been created
Are you sure you want to delete "My most important" ?
NOTE:
Don't have an account? Register Here
<h1>Understanding Residency Under Article 4 of the DTAA: Criteria for Individuals and Entities Explained</h1> Article 4 of the Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement (DTAA) between two contracting states defines a 'resident' as any person subject to tax in a state due to domicile, residence, or similar criteria. It includes governments and local authorities, but excludes those taxed solely on income from sources within the state. For individuals deemed residents of both states, residency is determined by permanent home, center of vital interests, habitual abode, or nationality, with unresolved cases settled by mutual agreement. For entities, residency is based on the place of effective management, with disputes resolved by mutual agreement between states.