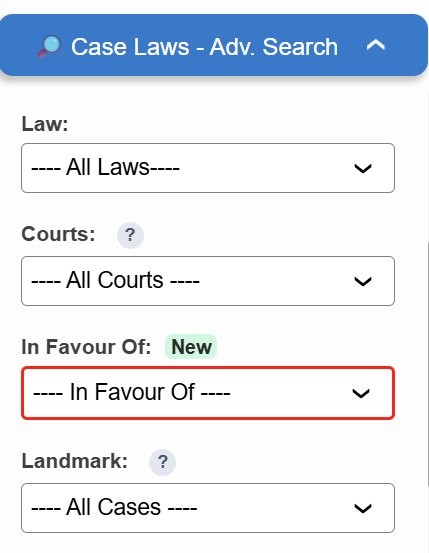
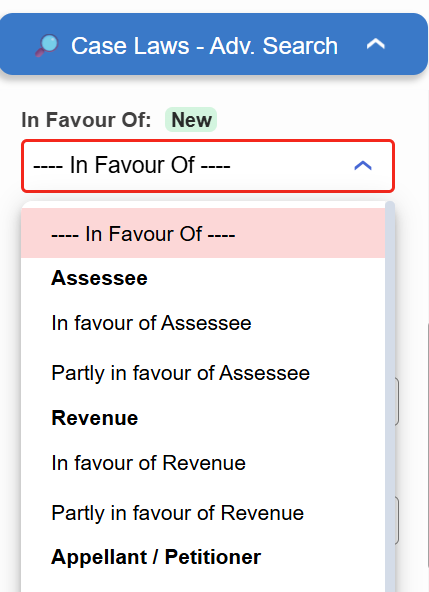
Introducing the “In Favour Of” filter in Case Laws.
- ⚖️ Instantly identify judgments decided in favour of the Assessee, Revenue, or Appellant
- 🔍 Narrow down results with higher precision
Try it now in Case Laws →
Just a moment...
Introducing the “In Favour Of” filter in Case Laws.
Try it now in Case Laws →


Press 'Enter' to add multiple search terms. Rules for Better Search
No Folders have been created
Are you sure you want to delete "My most important" ?
NOTE:
Don't have an account? Register Here
<h1>24th Amendment Act, 1971: Parliament Gains Power to Amend Fundamental Rights, Clarifies Process in Article 368.</h1> The Constitution (24th Amendment) Act, 1971, was introduced following the Supreme Court's decision in Golak Nath's case, which limited Parliament's power to amend the Constitution, particularly concerning fundamental rights in Part III. The amendment aims to explicitly empower Parliament to amend any part of the Constitution, including fundamental rights, to align with the Directive Principles of State Policy and the Preamble's objectives. It proposes changes to Article 368 to clarify the amendment process and requires the President to assent to Constitution Amendment Bills. Additionally, it seeks to amend Article 13 to exclude its applicability to constitutional amendments under Article 368.