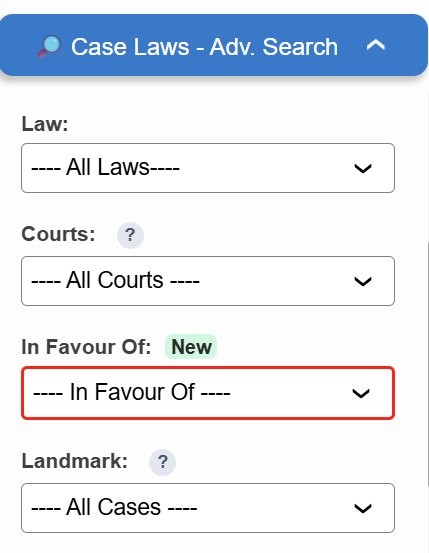
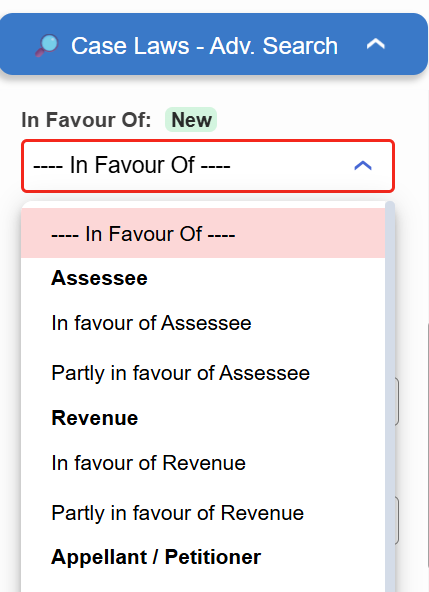
Introducing the “In Favour Of” filter in Case Laws.
- ⚖️ Instantly identify judgments decided in favour of the Assessee, Revenue, or Appellant
- 🔍 Narrow down results with higher precision
Try it now in Case Laws →
Just a moment...
Introducing the “In Favour Of” filter in Case Laws.
Try it now in Case Laws →


Press 'Enter' to add multiple search terms. Rules for Better Search
No Folders have been created
Are you sure you want to delete "My most important" ?
NOTE:
Don't have an account? Register Here
<h1>Income Taxation Rules for Cross-Border Employment: Key 183-Day Rule and Exceptions Explained</h1> Salaries, wages, and similar remuneration earned by a resident of one Contracting State are generally taxable only in that State unless the employment is conducted in the other Contracting State. In such cases, the income may be taxable in the other State. However, if the individual is present in the other State for no more than 183 days within a twelve-month period, and the remuneration is paid by a non-resident employer and not linked to a permanent establishment in the other State, it remains taxable only in the first State. Income from employment on ships or aircraft in international traffic may be taxed by the State of the enterprise operating them.